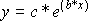
where c and b are constants.
A trendline can be added to only to the these chart types: bar, column, stacked column, scatter, line, and area.
Syntax
CHART.TREND(type, ord_per, forecast, backcast, intercept, equation, r_squared, name)
Type is the type of trend or regression.
| Number | Type used |
| 1 | Linear |
| 2 | Logarithmic |
| 3 | Polynomial |
| 4 | Power |
| 5 | Exponential |
| 6 | Moving Average |
Ord_per depends on type. If type is 3, then ord_per is the order of the polynomial. If type is 6, ord_per is the number of periods for the moving average. If type is neither 3 nor 6, then ord_per is ignored.
Forecast is the number of periods or units to extrapolate the trendline in the positive or forward direction. This argument is ignored for moving averages (type 6). The default is zero.
Backcast is a number specifying the number of periods or units to extrapolate the trendline in the negative or backward direction. This argument is ignored for moving averages (type 6). The default is zero.
Intercept is a number specifying the value of the y-intercept of the trendline, if it is already known. If FALSE or omitted, Microsoft Excel will calculate the y-intercept . This argument is ignored for moving averages.
Equation is a logical value specifying whether the trend equation should be displayed on the chart. If TRUE, the equation will be displayed on the chart. If FALSE or omitted, the equation will not be displayed on the chart.
R_squared is a logical value specifying whether the r-squared equation should be displayed on the chart. If TRUE, the value will be displayed on the chart. If FALSE or omitted, the equation will not be displayed on the chart.
Name is a text string specifying the custom name of the trendline. Can also be a logical value. If TRUE or omitted, the automatic name will be used instead.
Remarks
A trendline can not be added to a 3-D chart, a stacked chart, or an 100% chart.
The linear model calculates the least squares fit for a line represented by the equation y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the intercept.
The logarithmic model calculates the least squares fit through points using the equation y = c*ln(x) + b, where c and b are constants.
The exponential model calculates the least squares fit through points using the following equation:
where c and b are constants.
The polynomial model calculates the least squares fit through points using the following equation:
where b, c1, c2, c3, etc. are constants.
The power model calculates the least squares fit through points using the following equation:
where b and c are constants.
Related Function
CHART.WIZARD Equivalent to clicking the ChartWizard button on the Standard toolbar
Return to index